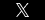In Myocaritis in Children: A Diagnosis to Consider in the Pediatric Emergency Department, a board certified pediatric emergency medicine expert witness explains that myocarditis, or inflammation of the heart muscle, may result in significant heart malfunction or death. This is a condition that may result in misdiagnosis and is important for the pediatric emergency medicine physician to be familiar with and consider.
In children, the most common reason is due to a viral infection. Other causes include Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, toxic shock syndrome, fungus infections and or parasites.
Since myocarditis in children may mimic other conditions, the diagnosis of myocarditis is challenging. It is a rare condition, with common symptoms that the pediatric emergency medicine provider may encounter with other common conditions.
Consider myocarditis on the differential when a child presents with trouble feeding or tachypnea (breathing fast). Young babies may be difficult to calm and described as fussy. On exam, infants and children may have hypo-perfusion presenting with cool and pale extremities.
Although some children may have more overt signs such as swelling in the face, feet or the legs, general flu-like symptoms may be the only sign of myocarditis.
Myocarditis is a clinical diagnosis and requires a careful history and thorough physical examination. The pediatric emergency medicine doctor may order a chest x-ray that reveals an enlarged heart size or fluid in the lungs. Similarly, an electrocardiogram may reveal abnormal heart electrical activity. Finally, an echocardiogram may reveal increased heart size.
Given that other organs may be affected by myocarditis, it is important to assess kidney and liver function. Also, given the infectious causes, a blood count and tests for infections may also be done.
Myocarditis in babies and children requires admission to an intensive care unit management.
Read more: Pediatric Emergency Medicine Consultants
 Expert Witness Blog
Expert Witness Blog